[email protected]
+91 97269 26402
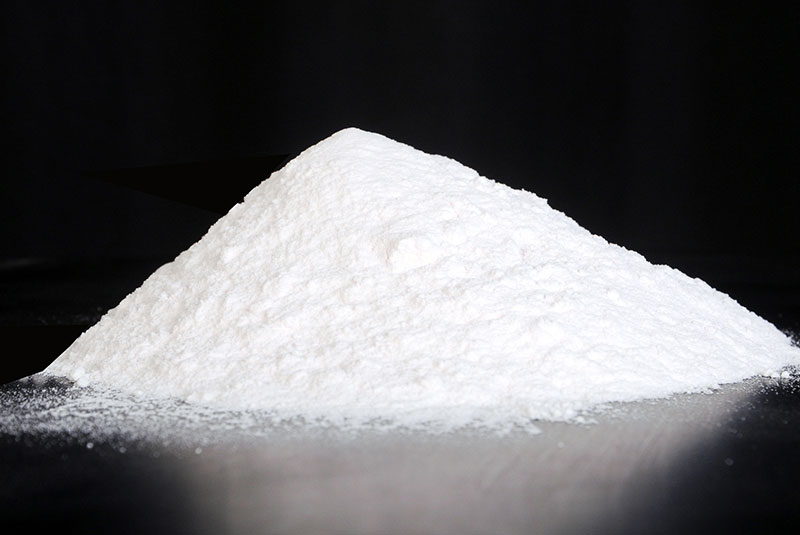

Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate
Product Name: Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate
Molecular formula: ZnSO4.H2O
CAS NO.: 7446-19-7
Appearance: White Powder
Grad: Agriculture, Technical Grade, Feed Grade
We are chiefly engaged in manufacturing and supplying the best quality Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate. Required for curing the mineral deficiency in crops, our Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate is the best choice available in the markets. The Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate that we provide is especially formulated by reacting zinc with light aqueous sulfuric acid. Available in varied packing options.
Applications
- Chemical industry
- Textile and leather industry
- Agriculture industry
- Pigment industry
- Animal Feed
- Poultry Feed
Packaging
- 1 kg – Polyester laminated or LDPE pouches
- 5 kg – Laminated HDPE bags with LDPE liner or LDPE laminated polyester pouches
- 10 kg, 25 kg, 50 kg – Laminated HDPE bag
Chemical Properties :
| Zinc (Zn), % weight | 33.0 Min. |
| Copper (Cu) weight | 0.1 Max. |
| Lead (Pb) weight | 0.003 Max. |
| Magnesium (Mg) weight | 0.002 Max. |
| pH not less than | 4.0 |
| Solubility in water weight | 99.0 Min. |
Physical Properties :
| Zinc (Zn), % weight | Free flowing white vitriol powder |
| Appearance | White Powder |
| Chemical Formula | ZnSo4.H2o |
| Molecular Weight | 179.46 |
| Density | 3.28 gm/cm3 (205 lbs/ft3) |
| Solubility in water weight | Transition at 238°C (460°F) |
| Solubility in 100 parts of water | 89.5 at 100°C (212°F) |
Our Product Range
|
Items |
Specification |
|||||
|
I Type (Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate) |
||||||
|
High-Class |
First-Class |
Qualifier |
||||
|
( calculate Zn ) Main content |
35.7 |
35.34 |
34.61 |
|||
|
Assay |
99.0 |
98.5 |
98.0 |
|||
|
Insoluble matter content ≤% |
0.020 |
0.050 |
0.10 |
|||
|
PH value ( 50g /L ) ≥% |
4.0 |
4.0 |
—— |
|||
|
Chloride ( Cl ) content ≤% |
0.20 |
0.60 |
—— |
|||
|
( Pb ) content ≤% |
0.002 |
0.007 |
0.010 |
|||
|
( Fe ) content ≤% |
0.008 |
0.020 |
0.060 |
|||
|
( Mn ) content ≤% |
0.01 |
0.03 |
0.05 |
|||
|
( Cd ) content ≤% |
0.002 |
0.007 |
0.010 |
|||
|
( Cu ) content ≤% |
0.001 |
—— |
—— |
|||

Introduction
- Zinc importance in plant nutrition is recognized after the introduction of
high yielding varieties. - Zinc deficiency caused by intensive cropping.
- 80% of rice land deficient in zinc.
- After N and P zinc playing an important role in rice.
Role in Plant System
- Producing several enzymes
- Responsible for chlorophyll formation.
- Deficiency reduce photosynthetic activity.
- Playing a role in N – metabolism.
- Regulate auxin (hormone) production
- Promotes nucleic acid production for protein synthesis.
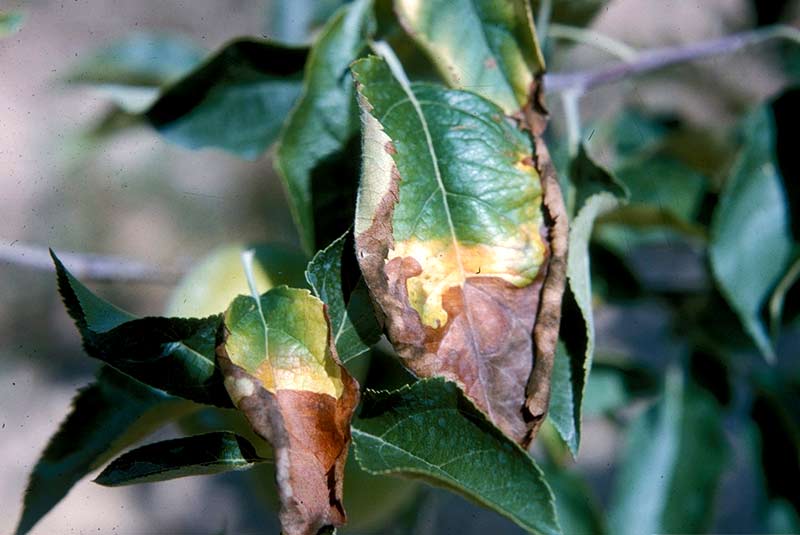


Injury Due To Excess Fertilizer
- Excess zinc cause deficiency of Iron.
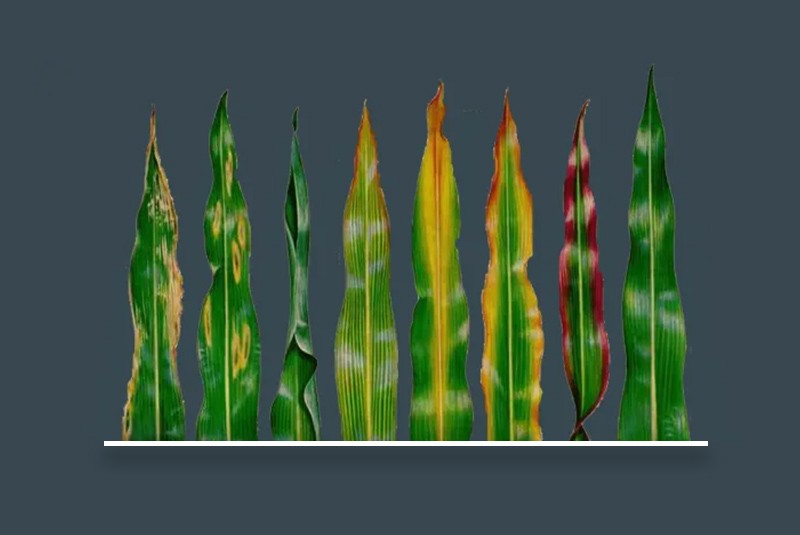
Deficiency Symptoms
- Appearance of rusty brown spots and discoloration of older leaves starting from 2-3 weeks after planting.
- Uneven crop stand.
- Under acute conditions margins of older leaves dry up.
- Under acute conditions margins of older leaves dry up.
- Tillering and growth adversely affected (KHAIRA disease)
- Fresh leaves smaller in size.
- No uniform maturity of crop.
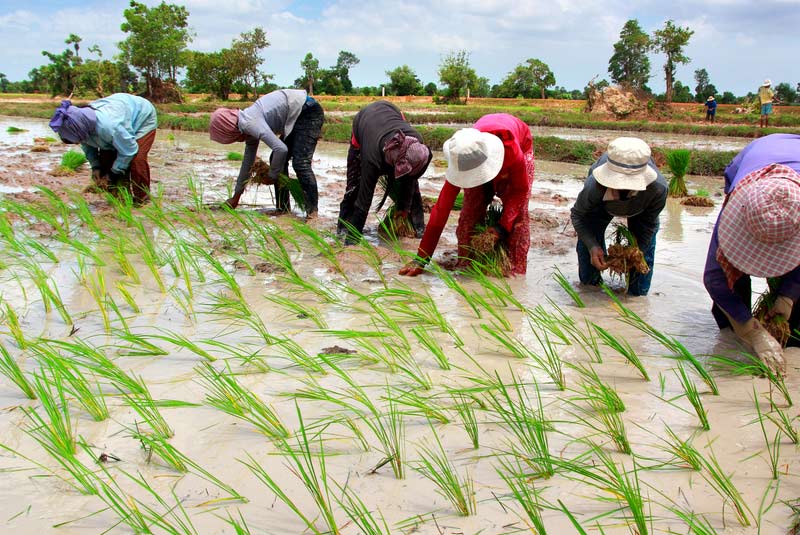

Management of Zinc for Rice
- 50 kg of Zinc Sulphate /hector to soil in the final puddling in every Rabi season in double cropped wet lands.
- Once in 2-3 crops in single cropped areas.
- Give a gap of 4-5 days between application of phosphorus and Zinc since Zn has antogonistic effect with phosphorus.
- Zinc deficiency in standing crop can be corrected by spraying 0.2% zinc sulphate solution (2g/lt of water) about 500 liters of spray solution is required to cover one hectare.
- Spraying should be repeated 2-4 times at an interval of 5-10 days
Sources:
- Zinc Sulphate – Zn SO4 7H2O (21%Zn)
- ZnSO4 H2O (33% Zn)
- Chelated Zinc (12% Zn) – is costly
- Chelated Zinc (14% Zn)



